Lupine Publishers | Advancements in Cardiology Research & Reports
Abstract
Psychopathy of the careerist is a developmental disorder marked by
emotional deficits and an increased risk for antisocial
behavior. It is not equivalent to the diagnosis Antisocial Personality
Disorder, which concentrates only on the increased risk for
antisocial behavior and not a specific cause-ie, the reduced empathy and
guilt that constitutes the emotional deficit. Our review
considers data regarding the neurobiology of this disorder. Dysfunction
within the amygdala’s role in reinforcement learning and
the role of ventromedial frontal cortex in the representation of
reinforcement value is stressed. Data is also presented indicating
potential difficulties within parts of temporal and posterior cingulate
cortex. Suggestions are made with respect to why these
deficits lead to the development of the disorder. Knowledge of recent
neuorobiology is proving our thesis that Darwin was wrong
when formulated his theorem„ Survival of the fittest“. Reality in 21
century is showing that “Survival of the careerist“ based on the
Quantum Entanglement Entropy (QEE) is more valid principle of Social
Dynamics in our days. Careeristic Competition is the main
cause of the QEE leading to icreased complications through Coincidenses
of Social Dynamics.
Keywords: Psychopathy; Amygdala; Ventromedial Frontal Cortex; Emotion; Careerist; Quantum Entanglement Entropy (QEE);
Social Dynamics
Psychopathy of the careerists is a disorder characterized by
pronounced emotional deficits, marked by reduction in guilt and
empathy, and involves increased risk for displaying antisocial
behavior. The disorder is developmental Cicchetti & Dawson [1].
Psychopathic traits, particularly the emotional component, are
relatively stable from childhood into adulthood. One reason for
the attention this classification receives is its strong predictive
utility for institutional adjustment and recidivism (ie, reoffending).
Individuals with psychopathy are approximately three times more
likely to reoffend than those with low psychopathic traits, and
four times more likely to reoffend violently. Admittedly, it is the
past antisocial behavior, indexed by psychopathy assessments,
that is particularly important in predicting future criminal
activity. However, it is the emotional component that characterizes
psychopathy; high levels of antisocial behavior can develop from
other neurobiological and socio-environmental risk factors
Koenigs [2]. Psychopathy is not equivalent to the DSM-IV diagnosis
of conduct disorder or antisocial personality disorder (ASPD)
or their ICD-10 counterparts. The psychiatric diagnoses focus on
antisocial behavior rather than underlying causes; ie, the emotion
dysfunction seen in psychopathy. Individuals meeting the criteria
for antisocial personality disorder are more heterogeneous in their
pathophysiology than individuals meeting criteria for careerist
psychopathy.
Psychopathy as a Careerist Disorder of Attention
According to the response modulation hypothesis, the difficulty
faced by individuals with psychopathy relates to a problem in
reallocating attention to secondary information when engaged in
goal-directed behavior. This difficulty in balancing the demands of
goal-directed processing and secondary information processing
creates a bias whereby psychopathic individuals are less responsive
to affective information unless it is a central aspect of their
goal-directed focus of attention. It is argued that “psychopathic
individuals initially perceive and identify both primary and
secondary information, but are particularly adept at using higherorder
processes to resolve the competition between goal-relevant
and secondary demands on attention”. The authors argue that
these higher-order processes create an “early attention bottleneck” that limits the processing of secondary information Newman
[3]. Typically, an early attention bottleneck has implied that only
physical and not abstract properties of a secondary stimulus are
processed; the bottleneck occurs within the visual stream, with
“early” processing corresponding to physical feature as opposed to
abstract feature processing. However, Newman and colleagues use
the term in a temporal sense; processing by higher order processes
of the first stimulus in a sequence of stimuli acts as a bottleneck for
processing the second stimulus in a sequence Baskin-Sommers [4].
It is clear that regions implicated in top-down attentional
control (ie, higher order attentional processes), such as lateral
frontal, dorsomedial, and parietal cortices, impact the amygdala’s
response to emotional stimuli. Increased priming of taskrelevant
representations by these regions is thought to reduce
the representational strength of emotional stimuli within
temporal cortex, following representational competition, and
consequently reduce amygdala responses to these stimuli. In
short, the reduced emotional responsiveness of individuals with
elevated psychopathic traits could be a secondary consequence
of heightened top-down attentional control to non-emotional
stimulus features. In recent studies in adults with psychopathy,
Newman and colleagues manipulated attention either towards the
threat-relevant component of a stimulus array or away from this
component and examined fear-potentiated startle (FPS). In each
of these studies, psychopathy scores were significantly inversely
related to FPS under conditions that required participants to focus
on a threat-irrelevant dimension of stimuli.
In contrast, psychopathy scores were unrelated to FPS when
attention was focused on the threat-relevant dimension Hare [5].
These studies provide important support for the suggestion that it
is an attentional abnormality, rather than a problem in emotional
responding, that is central to an understanding of psychopathy.
Given the literature on the interaction of top-down attentional
control and emotional responding, these data should suggest
that psychopathy is related to enhanced recruitment of regions
implicated in top-down attentional control (ie, dorsomedial and
lateral frontal and parietal cortices). The stronger these are recruited
(as a function of psychopathy), the stronger the priming of threat
irrelevant stimulus dimensions, the weaker the representation of
threat relevant stimulus dimensions following representational
competition, and the weaker the emotional response Blair [6].
Emotion-Based Accounts of the Careerist
Adults with psychopathy show a variety of emotional processing
impairments. For example, they show:
i) Reduced autonomic responses to the pain and distress of
others.
ii) Reduced recognition of emotional expressions (for metaanalytic
reviews of this literature, see refs 35,36). Interestingly,
this impairment is relatively selective. Recognition of fearful,
sad, and happy expressions is clearly reduced, while the
recognition of disgusted and angry expressions remains intact.
iii) Reduced aversive conditioning; they are less likely to
show autonomic activity to stimuli associated with shock.
iv) Pronounced difficulties with reinforcement based
decision-making.
These are seen in:
a) Extinction: Where the participant learns to respond to
a stimulus for reward but, after a set number of trials, this
responding must be extinguished because the reinforcement
contingencies have changed and the response is no longer
rewarded.
b) Reversal Learning: Where the participant learns to make
one form of response to a pair of stimuli to gain a reward but,
after a set number of trials, this response must change, due to
a change in reinforcement contingency, in order to gain the
reward.
c) Economic Decision-Making Paradigms: The Ultimatum
game involves the participant and another individual. The
participant has to decide whether to accept the offer of a share
of resources made by the individual. This can be fair (eg, making
a 50:50 split on $20 so each gains $10) or progressively unfair
(eg, only $4 is offered to the participant). Individuals with
psychopathy show increased rejection of unfair offers, even at
cost to themselves, relative to comparison individuals.
d) Moral Judgment: Individuals with psychopathy show
reduced responsiveness to what can be termed “care-based”
transgressions (ie, transgressions involving harm to another;
eg, one person hitting another). This has been seen using a
variety of paradigms. Again this impairment in transgression
processing is selective. Care-based transgressions are reliant
on appropriate responsiveness to the pain and distress of
others. As noted above, this is dysfunctional in adults with
psychopathy. In contrast, conventional transgressions (reliant
on authority; eg, talking in class) are reliant on appropriate
responsiveness to other individual’s anger while disgust-based
transgressions (that can cover aspects of sexual behavior) are
reliant on appropriate responsiveness of other individual’s
disgust.) Adults with psychopathy show intact processing of
these emotional expressions. They also show intact processing
of these forms of transgression Munoz & Frick [7].
Given these data, a variety of authors have suggested that an
emotional dysfunction underpins the deficits seen in individuals
with psychopathy. The oldest of these positions suggested that
punishment processing was dysfunctional while reward processing
was intact or even possibly superior. It is now clear that the situation
is considerably more complicated. Three critical data points are important to note. First, the expression impairment is not seen
for all aversive expressions; it is seen for fear and sadness but not
anger and disgust. This is inconsistent with a general impairment
in processing aversive stimuli. Second, the expression processing
impairment is also seen for happy expressions. This suggests that
the processing of rewarded stimuli is also disrupted. Third, the
immediate response to punishment is intact in adults with careerist
psychopathy.
Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging (Smri) Studies Of Careerist
A series of findings, reported across labs where appropriate
IQ comparisons have been made, are worth noting. Not all studies
have reported reduced volumes in these regions in psychopathy
but none (at least involving IQ matched samples) have reported
increased volumes in these regions. Thus, three studies have
reported reduced amygdala volumes in adults with psychopathy
including the largest structural imaging study of this population
to date (N=296). Similarly, four studies have reported reductions
in temporal pole and two in STS. Three studies have reported
reductions in orbitofrontal cortex. Moreover, and interestingly
given the extensive connections between the amygdala and
orbitofrontal cortex though the uncinate fasciculus white matter
tract, all three DTI studies examining the structural integrity of
this tract in individuals with psychopathy have reported reduced
structural integrity relative to comparison individuals.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (FMRI) Studies Of Careerist
Regrettably, again, many of the functional MRI (fMRI) studies
of psychopathy, even when IQ was assessed (as an IQ<80 was
exclusory), did not report that groups were matched for IQ making
their interpretation problematic. Consequently, the data from
such studies will not be considered here. However, studies where
appropriate IQ matching was conducted include investigations
of moral judgment, expression processing, emotional memory,
processing abstract and concrete words, emotional Theory of Mind,
and connectivity mapping. Several of these studies support the sMRI
findings of core dysfunction in the amygdala. Thus, individuals with
psychopathy have been reported to show amygdala activity during
moral judgment and also a weaker positive association between
amygdala activity and severity ratings of transgressions than is seen
in healthy individuals. In addition, violent schizophrenic patients
with psychopathy show reduced amygdala responses to fearful
expressions-though a relationship between psychopathic traits in
aggressive individuals and amygdala responsiveness was not seen
in another study. In addition, a reduction in amygdala activity was
seen during an emotional memory paradigm. Currently, though
the literature with respect to orbital/ventromedial frontal cortex
(vmPFC) is less convincing. One study reported a reduction in
the differential responsiveness of vmPFC to moral and nonmoral
images.
However, a second study reported increased vmPFC responses
in individuals with psychopathy when performing a task involving
the identification of other individual’s emotional responsiveness
(this increased vmPFC responsiveness did not relate to the
emotional content as it was also seen in the non-emotional
control condition). Notably, though, studies have shown weaker
functional connectivity between vmPFC and the amygdala and
between vmPFC and posterior cingulate cortex. Given the findings
of reductions in the temporal pole, it is interesting to note that
studies have reported reduced responsiveness within this region
to moral transgressions and abstract words. There have also been
two reports of reduced posterior cingulate cortex responsiveness:
during the processing of moral transgressions and emotional
memory. In addition, posterior cingulate cortex shows reduced
connectivity with vmPFC and regions of posterior cortex engaged
in visual representation and attention priming. Two studies have
also observed anomalous responsiveness within rostral medial
frontal cortex. Thus, one study showed reduced activity within this
region during moral judgment with increasing psychopathic traits.
A second showed increased activity within this region relative
to comparison individuals to judgments concerning vignette
character’s emotional states of careerist.
Psychopathy of The Careerists Is a Serious Developmental Disorder Marked by Pronounced Emotional Dysfunction And An Increased Risk For Aggression
It is not equivalent to antisocial personality disorder from
DSM-IV-R. Individuals meeting criteria for psychopathy with
gold standard assessment techniques will also meet criteria for
antisocial personality disorder. However, many other individuals
with antisocial personality disorder will not meet criteria for
psychopathy. It is argued here that the emotion dysfunction
relates to three core functional impairments: in the association of
stimuli with reinforcement, the representation of expected value
information and in prediction error signaling. These impairments
are thought to relate to the observed dysfunction seen in both sMRI
and fMRI studies within the amygdala, vmPFC, and (currently only
in work with youth samples) striatum. Other regions of temporal
cortex (temporal pole and superior temporal sulcus) may also be
dysfunctional—though whether this reflects primary pathology
or the secondary, developmental impact of dysfunction in the core
regions is unclear. It is also unclear whether any functions reliant
on these regions are detrimentally affected in careerist individuals
with psychopathy. Finally, there is sMRI and fMRI evidence of
posterior cingulate cortex dysfunction. This is interesting given
the extensive connectivity of this region with vmPFC and also
its shared overlap in function. Both regions are implicated in the
representation of expected value. However, as yet, no studies have
formally investigated the representation of expected value within
posterior cingulate cortex in adults with psychopathy of careerist.
Importantly, by specifying the computational and neural
systems level impairments that are associated with this disorder,
we now have available biomarkers of dysfunction. Such biomarkers
are not only of potential use in diagnostic classification—the
functional impairments in one aggressive patient may be very
different from those of another—but also for assessing treatment
efficacy. Currently, this disorder is regarded as extremely difficult to
treat. Moreover, treatment studies are difficult when the outcome
measure may be reoffending or incidence of aggressive episodes.
However, with appropriate biomarkers it becomes possible to use
these to determine treatment efficacy. The field is currently at this
exciting stage. Now we need to identify effective treatments Blair
[6], Blair [8]. A study of office politics suggests that workplaces
are a jungle of awkward personalities vying for domination.
Oliver James, the psychologist and broadcaster, identified three
types of dysfunctional personalities among white collar workers:
psychopath, Machiavellian, and narcissist Lynam [9]. These are the
colleagues who have no compunction about trampling over others,
or like nothing more than to plot and scheme, or who drone on
endlessly about themselves. Most terrifyingly, the author concluded
that there was fourth dysfunctional type: a “triadic person” who
is a combination of all three. Such staff, James warns, have a
dangerous, yet effective mix of a lack of empathy, self-centredness,
deviousness and self-regard which can propel them to the top of
the organisations. Research has suggested that there has been an
increase in the “triadic” conditions over the past 30 years because
of changes in Western society and especially the rise of workplaces
where there are no objective criteria for success or failure.
In a book, Office Politics, James warns how people who do not
suffer from the disorders can lose out in the world of work and
damage their emotional health unless they learn how to survive
among such personalities. The warning may resonate among the
almost eight million Britons who work in offices, as well as those
based in schools, hospitals and particularly television studios —
James says broadcasting is infested with “triadic personalities”.
Describing psychopathic tendencies, Machiavellian cunning and
narcissistic selfishness a “dark triad”, James says: “This dark triad
of characteristics is very likely to be present in that person in your
office who causes you so much trouble. Whether you work in the
corporate sector, a small business or a public sector job, the system
you are in is liable to reward ruthless, selfish manipulation. James
adds: “Television is jam-packed with untalented people who have
managed to associated themselves with successful programmes
and disassociate themselves from failures.”
How To Tell If Your Boss Is Psychopathic, Machiavellian, A Narcissist or – Even Worse – All Three
For each character trait decide whether you strongly agree,
agree, feel it applies sometimes, disagree or strongly disagree and
give a score from 5 for strongly agree to 1 for strongly disagree.
The higher the score, the more they have combined psychopathic,
Machiavellian and narcissistic tendencies.
i) They tend to exploit and trick others for self-advancement.
ii) They have used lies and deception to get their way.
iii) They have used ingratiation to get their way.
iv) They tend to manipulate others for selfish reasons.
v) They tend not to feel regretful and apologetic after having
done wrong.
vi) They tend not to worry about whether their behaviour is
ethical.
vii) They tend to be lacking in empathy and crassly unaware
of the distress they can cause others.
viii) They tend to take a pretty dim view of humanity,
attributing nasty motives and selfishness.
ix) They tend to be hungry for admiration.
x) They tend to want to be the centre of attention.
xi) They tend to aim for higher status and signs of their
importance.
xii) They tend to take it for granted that other people will
make extra efforts to help them.
*Courtesy of Office Politics by Oliver James (Vermillion).
Mechanism of Psychopats Metastases Caused by the QEE
Sporadic colon cancer is caused predominantly by dietary
factors. We can select bile acids since high levels of hydrophobic
bile acids accompany a Western-style diet and play a key role in
colon carcinogenesis. Bile acid-induced stresses cause cell death
in susceptible cells, contribute to genomic instability in surviving
cells, impose Darwinian selection on survivors and enhance
initiation and progression to colon cancer. The most likely major
mechanism by which hydrophobic bile acids induce stresses on
cells is the Quantum Entanglement Entropy (QEE) metastases
through the DNA damage, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and
mitochondrial damage. Persistent exposure of colon epithelial
cells to hydrophobic bile acids can result by QEE in the activation
of pro-survival stress-response pathways, and the modulation of
genes/proteins associated with chromosome maintenance and
mitosis. The mechanism of QEE by which hydrophobic bile acids
contribute to genomic instability include oxidative DNA damage,
p53 and other mutations, micronuclei formation and aneuploidy.
Bile acids and oxidative stress decrease DNA repair proteins, an
increase in DNA damage and increased genomic instability through
this mechanism of metastases caused by Quantum Entanglement
Entropy. This process provides a mechanistic explanation for the
important QEE link between a Western-style diet and associated
increased levels of colon cancer Skopec I [10], Skopec [11], Skopec
[12], (Payne et al., 2008), Skopec [13].
Dichotomous Correlations of Career Adaptation
One prevalent description of translational medicine, first
introduced by the Institute of Medicine’s Clinical Research
Roundtable, highlights two roadblocks (i.e., distinct areas in need
of improvement): the first translational block (T1) prevents basic
research findings from being tested in a clinical setting; the second
translational block (T2) prevents proven interventions from
becoming standard practice. An important role in the processes
of adaptation and masking in humans is playing also the immune
system. The innate immune system functions as an interpreter of
tissue damage and provides a first line of defense, also translates
the information to other repair and defense systems in the body
by stimulating angiogenesis, wound repair, and activating adaptive
immunity. It is appropriate to consider autophagy a means for
programmed cell survival balancing and counter-regulating
apoptosis. Autophagy seems to have a dichotomous role in
tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Two other attributes play
a similarly paradox role. The first involves major reprogramming
of cellular energy metabolism in order to support continuous cell
growth and proliferation replacing the metabolic program that
operates in most normal tissues. The second involves active evasion
by cancer cells from attack and elimination by immune cells. This
capability highlights the dichotomous correlations of an immune
system that both antagonizes and enhances tumor development
and progression Walters [14]. Evidence began to accumulate in the
late 1990s confirming that the infiltration of neoplastic tissues by
cells of the immune system serves counter-intuitively to promote
tumor progression Skopec III [15].
The Bipolar Nature of Career: HYBRID, Twofaced New Main Law of Nature
The quantum entanglement is a basis of twofaced reality in
which we are living our lives. From this reality are outgoing also
the science and healthcare too. Although metastasis is important
for systemic correlations expansion (as in tumors), it is a highly
dichotomous process, with millions of cells being required to
disseminate to allow for the selection of cells-correlates aggressive
enough to survive the metastatic cascade. To quantify the dynamics
of metastasis of correlations development, we need look at the
coincidences of metastases in terms of co-occurrence at every point
of time Hemphill [16] To quantify co-occurrence we can use the φ
-correlation between dichotomous variables defined as:
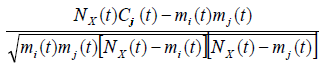 where Cj(𝓉) is the
number of co-occurrence at time t. Than i and j represent particular
site of metastasis, X represents the primary correlations type?
The pair-wise correlations (coincidences) between metastasis
network links for every primary correlation’s types and lead to the
correlation coefficient matrix.
where Cj(𝓉) is the
number of co-occurrence at time t. Than i and j represent particular
site of metastasis, X represents the primary correlations type?
The pair-wise correlations (coincidences) between metastasis
network links for every primary correlation’s types and lead to the
correlation coefficient matrix.
The dichotomous correlations of the adaptation may be caused
also by the Quantum Entanglement Relative Entropy as a measure of
distinguishability between two quantum states in the same Hilbert
space. The relative entropy of two density matrices P0 and P1 is
defined as 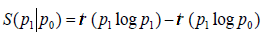 . When P0 and P1 are reduced density matrices on a spatial domain D for two states
of a quantum field theory (QFT), implies that S(P0|P1) increases
with the size of D. Than
. When P0 and P1 are reduced density matrices on a spatial domain D for two states
of a quantum field theory (QFT), implies that S(P0|P1) increases
with the size of D. Than 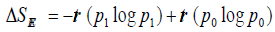 is the
change in entanglement entropy across D as one goes between the
states.
is the
change in entanglement entropy across D as one goes between the
states.
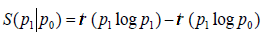 . When P0 and P1 are reduced density matrices on a spatial domain D for two states
of a quantum field theory (QFT), implies that S(P0|P1) increases
with the size of D. Than
. When P0 and P1 are reduced density matrices on a spatial domain D for two states
of a quantum field theory (QFT), implies that S(P0|P1) increases
with the size of D. Than 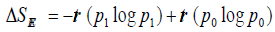 is the
change in entanglement entropy across D as one goes between the
states.
is the
change in entanglement entropy across D as one goes between the
states.
When the states under comparison are close, the positivity is
saturated to leading order: 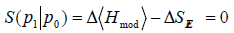 Skopec
II [17]. The problem of conventional adaptation may be given
by a definition of static, deterministic world. The proliferative
correlations lead to the resonances between the degrees of
freedom. When we increase the value of energy, we increase the
regions where randomness prevails. For some critical value of
energy, chaos appears over time we observe the exponential
divergence of neighboring trajectories. For fully developed chaos,
the cloud of points generated by a trajectory leads to diffusion. Here
we must as first formulate a new Main Natural Law: the HYBRID
Quantum Entanglement Entropy (HQEE) Skopec III [15]. Through
above resonances the QEE is causing a metastasis of correlations,
antagonistically intertwining (coincidences) all types of potentially
conflicting interests in cancer.
Skopec
II [17]. The problem of conventional adaptation may be given
by a definition of static, deterministic world. The proliferative
correlations lead to the resonances between the degrees of
freedom. When we increase the value of energy, we increase the
regions where randomness prevails. For some critical value of
energy, chaos appears over time we observe the exponential
divergence of neighboring trajectories. For fully developed chaos,
the cloud of points generated by a trajectory leads to diffusion. Here
we must as first formulate a new Main Natural Law: the HYBRID
Quantum Entanglement Entropy (HQEE) Skopec III [15]. Through
above resonances the QEE is causing a metastasis of correlations,
antagonistically intertwining (coincidences) all types of potentially
conflicting interests in cancer.
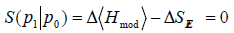 Skopec
II [17]. The problem of conventional adaptation may be given
by a definition of static, deterministic world. The proliferative
correlations lead to the resonances between the degrees of
freedom. When we increase the value of energy, we increase the
regions where randomness prevails. For some critical value of
energy, chaos appears over time we observe the exponential
divergence of neighboring trajectories. For fully developed chaos,
the cloud of points generated by a trajectory leads to diffusion. Here
we must as first formulate a new Main Natural Law: the HYBRID
Quantum Entanglement Entropy (HQEE) Skopec III [15]. Through
above resonances the QEE is causing a metastasis of correlations,
antagonistically intertwining (coincidences) all types of potentially
conflicting interests in cancer.
Skopec
II [17]. The problem of conventional adaptation may be given
by a definition of static, deterministic world. The proliferative
correlations lead to the resonances between the degrees of
freedom. When we increase the value of energy, we increase the
regions where randomness prevails. For some critical value of
energy, chaos appears over time we observe the exponential
divergence of neighboring trajectories. For fully developed chaos,
the cloud of points generated by a trajectory leads to diffusion. Here
we must as first formulate a new Main Natural Law: the HYBRID
Quantum Entanglement Entropy (HQEE) Skopec III [15]. Through
above resonances the QEE is causing a metastasis of correlations,
antagonistically intertwining (coincidences) all types of potentially
conflicting interests in cancer.
Throughout history, psychopaths, sociopaths, narcissists,
and assorted antisocial-personality-disordered individuals have
ruled societies Blair [8]. Psychopaths and sociopaths often exhibit
glibness and superficial charm, have a grandiose sense of self-worth,
are pathological liars, display extreme narcissism, are deceitful,
cunning and manipulative, exhibit a lack of remorse or guilt, show
a callous disregard for the feelings of others, have no conscience,
lack empathy, and fail to accept responsibility for their actions. In a
Careeristic Competitive World, the people who act immorally, who
have no regard for truth, are going to have an advantage over those
who play by the rules. The result is that those who achieve positions
of power will be the most ruthless, the most sociopathic, the ones
without conscience. In societies run by psychopaths, ambitious
individuals and sycophants, who are not clinically psychopathic, are
induced to model themselves after powerful psychopaths in order
to achieve power. The result: psychopaths breed more psychopaths.
When corporate leaders, bankers, media executives, academics,
military officers, government officials, Congressmen and Senators
may be liars and deceivers, ruthless, callous manipulators who
have no regard for truth or other people, the entire fabric of society
is twisted in their image, and psychopathic behavior of carerists
becomes the norm.
Our world is characterized by: permanent war, and tendency
to full-spectrum dominance in Global Government, and the New
World Order. It is clear that this world has not been built by caring
human beings, but has been constructed and is run by powerful
hallow soulless individuals. And, despite the violence, suffering
and chaos they have caused, we allow them to remain at the top,
and in control. Knowledge of recent neuorobiology is proving
our thesis that Charles Darwin was wrong when formulated his
theorem „Survival of the fittest“. It was the biggest false myth of
the modern science. As we have demonstrated in our above study,
the careerist is psychopat and not „the fittest“. From this reason we
must to correct Charles Darwin to „Survival of the careerist“. Reality
in 21 century is showing that Survival of the careerist based on the
Quantum Entanglement Entropy (QEE) is more valid principle
of Social Dynamics in our days. Careeristic Competition is the
main cause of the QEE leading to icreased complications through
Coincidenses of Social Dynamics.
For
more Lupine Publishers Open
Access Journals Please visit our website

No comments:
Post a Comment